The concept of crypto-currency such as Bitcoin has taken the world by storm for quite some time now. However, not every one of us is aware of the technology that drives this next big thing. If you have been following the news about cryptocurrency, you must be familiar with the term “Blockchain.” But what exactly is this “Blockchain?” Let’s find out.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain, as the name suggests, is a chain of blocks, only more complex. According to Blockgeeks, blockchain is a “time-stamped series of immutable record of data” which is managed by a large number of “computers not owned by any single entity.” Furthermore, each of these “blocks of data” is secured and bound to each other using “cryptographic principles” (chain).
Was that too hard to understand? Let’s make it simpler for you.
Take any digital piece of information like the details about your latest online purchase. Now, an online purchase requires several layers of verification. That involves the participation of a number of computers to check whether the transaction is happening as you prompted or not.
Once the transaction is done, the information is stored in a block, which is then added to the blockchain. The information stored in the blockchain becomes publicly available for anyone to view. You can access the information anytime, and learn when, where and by whom the block was added to the blockchain.
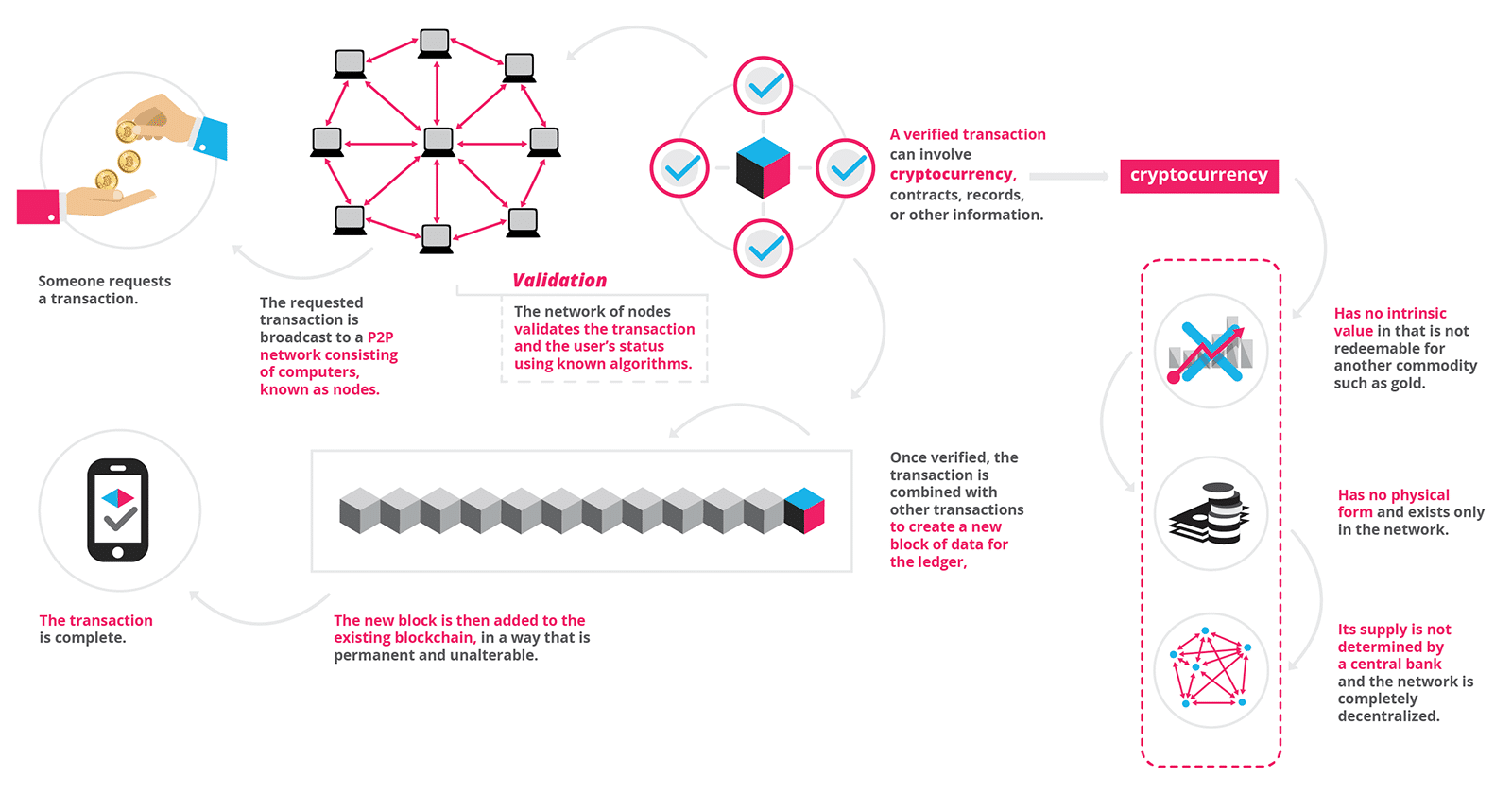
Now the question remains, “Is Blockchain secure?” We have just said that the content of the blockchain is accessible to anyone. Then how does that make it secure? Again, it’s more complicated than what you have heard about online data theft.
How secure Blockchain technology is?
Users have the option to connect their computers to a blockchain network. Every computer in the network has its own copy of the blockchain. Now, imagine thousands of users having individual copies of the blockchain. In the case of Bitcoin, the number of copies is in millions.
Even though every copy of blockchain is identical, it becomes difficult for anyone to manipulate information that is spread across a network of computers. If a hacker needs to manipulate a piece of information in the blockchain, he needs to go through every copy of the blockchain on the network.
Moreover, you do not have access to information that may help you identify other users making transactions. The information blocks are always stored linearly and chronologically. That means, the latest piece of block is always added to the end of the blockchain. So, each of the blocks has its own position on the chain. This position is termed as “height”.
Interestingly, once a block is added to the blockchain, it is difficult to go back and modify the content of the block. Each block contains its own unique code termed “hash”, along with the hash of the previous block on the blockchain. If the information in a block is altered, the respective has code changes as well.
Now, how does that help secure the information stored in blockchain? Let’s assume that a hacker tries to modify the transaction details stored in a block for a reason. As soon as the hacker tries to edit the transaction details, the hash of the block will change simultaneously. To cover the tracks, the hacker needs to change the hash of the next block in the chain.
As you can guess, the hacker will have to change all the blocks’ hash in the blockchain to completely cover the tracks. Even if the hacker has the patience to edit all the hashes, recalculating the hashes will take a massive amount of computing power. Hash codes are created by a math function that converts digital information into a string of numbers and alphabets.
Basically, the effort and computation power required for hacking and manipulating blockchain outweigh the benefits. If you already know how to solve a math problem, would you avail assignment help for it? No, right? It’s the same for blockchain hacking. Nobody likes to deal with things where efforts cost higher than the reward.
What are the practical applications of blockchain technology?
We have discussed the part that the blockchain contains digital information about monetary transactions. However, the blocks in a blockchain can store data about other transactions as well. A recent survey done by Deloitte reveals that 34% of the companies are already using blockchain technology. Moreover, 41% of the surveyed companies are expected to deploy blockchain applications in the near future.
Banking sector
There is no other industry that will get more benefitted from blockchain technology than the banking industry. Most banks are operational only five days a week for limited hours. It is the reason why customers often need to wait for hours or even days to process a transaction. Since blockchain technology is available 24×7, this can process any transactions a lot faster, irrespective of the time and date. The same goes for stock trading business as well.
Cryptocurrency
Blockchain is the technology that drives the cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and others. Unlike conventional currencies, cryptocurrencies are not dependent on any bank or government. They work across the network of computers. Thanks to blockchain technology, the instability of the government or collapsing of a bank does not affect the cryptocurrency. Also, the piece of technology eliminates a number of processing and transaction fees for the users.
Property records
The registration and management of property records are tiresome tasks for anybody. Besides, if there is a property dispute, reconciling the claims to the property with the public index is both expensive and time-consuming. Also, there is a risk of human error in the record-keeping. Storing property ownership on blockchain can not only accelerate the registration process but also offer accurate information when it’s time.
Smart contracts
A smart contact is basically a computer program that is integrated with blockchain technology. This kind of programs operates under certain terms and conditions. Once the terms and conditions are met, the contract is carried out the way it was supposed to. Say, for example, you are renting an apartment using a smart contract. Once you pay the deposit as per the agreement, you receive the door code to the apartment.
Voting
Implementing blockchain technology into the electoral process can eliminate election fraud. Also, introducing blockchain in voting can also increase the voter turnout. Moreover, the technology can offer more transparency in the election. Not to forget, this will reduce the manpower required for conducting the election, and deliver instant results.
Supply chains
Suppliers now have the option to use blockchain to keep a record of the origins of purchased materials. This will help the companies verify the authenticity of the products while keeping track of the health and ethics labels like “Local”, “fair trade” and “organic”. Also, this technology can certify the legitimacy of the sold products. With blockchain technology, there is going to be transparency over the supply chain auditing for a range of consumer goods.
Parting words
Blockchain was introduced to the world in 1991 as a research project. Even though it didn’t get much recognition in its early stage, it is slowly making its way into the market. And with the rising number of practical applications, it won’t be wrong to infer that the technology is here to stay.
Mark Hales is a programmer by profession who is currently employed at a reputed MNC in Singapore. He is also associated with MyAssignmenthelp.com as an expert who offers assignment help to students on their request.



