Anxiety is part of our brain’s fight or flight response, so everyone experiences anxiety sometimes. It can help motivate you, push you to study for a test, rehearse before a performance, or even just get to work on time. However, when someone has an anxiety disorder, their anxious feelings do not go away, and they are typically out of proportion for the situation. In this article, we will look at everything you need to know about anxiety disorders.
What are anxiety disorders?
Anxiety disorders are a common mental health disorder that affects about 19 percent of adults in the United States. When someone has an anxiety disorder, feeling anxious is more or less a constant struggle that can impact every aspect of their lives.
The feeling of fear that comes with an anxiety disorder is often intense and can be debilitating. Someone with an anxiety disorder may be unable to do things they enjoy because of their anxiety; it can impact their jobs, relationships, and more. It is not something that someone can “get over,” nor is having anxiety a sign of a weak character, but it can be managed with medication.
Types of anxiety disorders
Not all anxiety disorders are the same; there are multiple different types of anxiety disorders. While they all have anxiety in common, each disorder has its own symptoms and characteristics.
-
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
One of the most commonly diagnosed types of anxiety disorders is generalized anxiety disorder. This disorder involves worrying excessively and feeling anxious about events or activities. It is hard to control, and the worry often shifts from one thing to another.
People with generalized anxiety disorder can feel anxious about their everyday lives, relationships, current events, and even “what if” scenarios of things that might occur.’
-
Panic Disorder
A panic disorder involves having persistent and intense panic attacks that can occur with little or no warning. A panic attack can come with feelings of extreme terror, a rapid heartbeat, and breathing heavily or hyperventilating. It can be hard to bring yourself out of a panic attack, but many who have this type of anxiety disorder can learn coping methods that help them get through panic attacks.
-
Agoraphobia
Agoraphobia is the extreme and irrational fear of being in a situation that you cannot escape. They will experience panic over being in public and try to avoid any situation that makes them feel trapped or helpless.
The avoidance behaviors that accompany agoraphobia can be life limiting. Someone with agoraphobia may avoid going shopping, driving, traveling, and other situations. In more extreme cases, the fear can be so severe that someone with this type of anxiety disorder is unable to leave their home.
-
Social Anxiety Disorder
Social anxiety disorder is the fear of being in social situations. This might be centered on events like public speaking, being in a crowded room, or it could be a more generalized fear of social situations. Those who have this type of anxiety disorder may feel like they are being overly scrutinized by others. They might also be overly critical of themselves and experience fear in different social situations.
The symptoms that can accompany social anxiety disorder include feelings of dread, shaking, an upset stomach, and a racing heartbeat, which will occur leading up to and during these situations. Those with this type of anxiety may choose to avoid these situations as much as possible.
-
Phobias
A phobia is an intense and irrational fear over a specific situation or thing that is overwhelming and out of proportion. They may experience crying, sweating, shaking, breathing rapidly, or a rapid heartbeat. This can, of course, lead to attempting to avoid the source of their fears. While sometimes, this is doable, it is not easy for someone with a fear of spiders to just avoid them forever; they will encounter them at some point, no matter how hard they try to avoid them.
-
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
Obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) is the unwanted thoughts and impulses that cause repetitive and routine behaviors as part of coping with your anxious feelings. Not all medical professionals consider OCD to be an anxiety disorder, but it does have symptoms that align with anxiety.
-
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can occur when someone experiences a traumatic event. They can experience fear, nightmares, sleep interruptions, flashbacks, and avoidance of the traumatic event. This is another mental health condition that not all professionals consider to be an anxiety disorder, but it does have many symptoms in common, even if it does not have quite the same source that most anxiety disorders do.
-
Separation Anxiety Disorder
Separation anxiety disorder is most common in young children, but it can affect people of all ages. When someone has separation anxiety disorder, they experience intense levels of anxiety when being away from a place or person that gives them the feeling of safety or security. It is most commonly seen by children who have separation anxiety from being away from one of their parents, especially the first few times that they are apart.
-
Selective Mutism
Selective mutism is an anxiety disorder that is typically developed in childhood, in the ages between two and four years old. Essentially, they experience fear, anxiety, or embarrassment that keeps them from speaking in certain settings, like around strangers or at school. This is accompanied by fidgeting, lacking expressions, or not making eye contact when in a situation that makes them feel anxious.
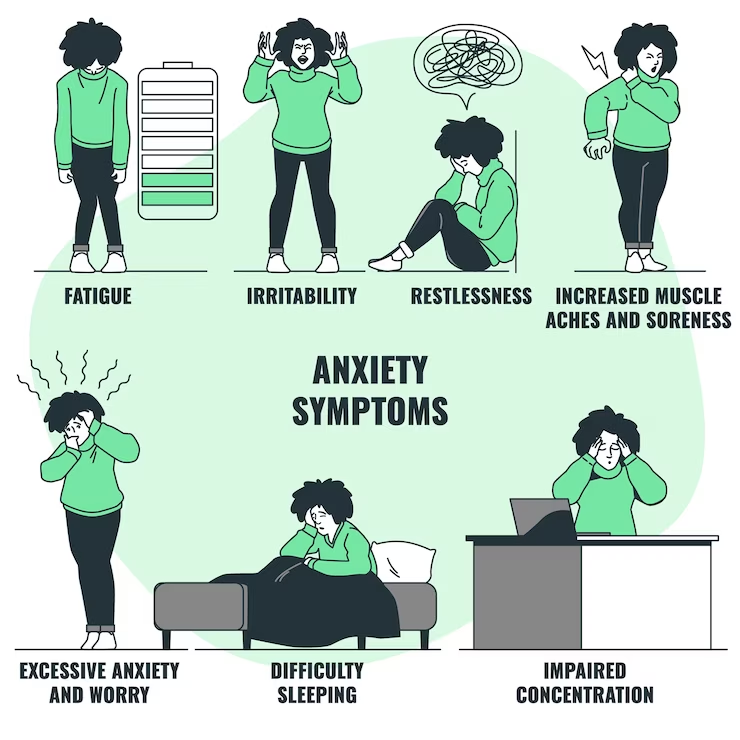
Symptoms of Anxiety Disorders
There are many different symptoms that accompany anxiety disorders, and no two people with the same type of disorder will experience the same symptoms. Every type of disorder also tends to have some symptoms that are unique to it. The symptoms that are generally common to anxiety disorders include:
- Dizziness
- Trouble sleeping
- Feeling nervous, scared, worried, panicked, or uneasy.
- Dry mouth
- Nausea
- Tight muscles
- Rapid heartbeat
- Unable to hold still.
- Sweaty or cold hands or feet
- Feeling powerless
- Feeling like something terrible is about to happen.
- Lightheaded
- Irritability
- Trouble concentrating
The reason for these symptoms is because they are part of your body’s natural fight or flight response. While this system is supposed to help someone avoid danger, when you have an anxiety disorder, the system is overworking on overdrive and doing more harm than good.
Causes of Anxiety Disorders
Millions of people of all ages experience an anxiety disorder at some point in their lives. While the exact causes of an anxiety disorder are not known yet, researchers have some ideas into what plays a role. Some of the factors that could be involved in an anxiety disorder are:
- Brain chemistry
- Stress
- Trauma
- Family history
- Medical conditions: many medical conditions, including those with chronic pain, are likely to develop an anxiety disorder.
- Environment
- Genetics
- Other mental health conditions: depression is linked to anxiety.
- Life-threatening events
- Substance use
- Withdrawing from alcohol or drugs
- Some personality types: low self-esteem, needing to be in control, or being a perfectionist.
How to Get Diagnosed with an Anxiety Disorder
While feeling anxious is a natural part of the body, if your anxious feelings are overly extreme, begin interfering with your life, or last for at least six months, it is a good idea to consider consulting your doctor.
Unfortunately, there is not a lab test to get you instantly diagnosed with an anxiety disorder, though doctors might still run some lab work to ensure there is not anything else going on with you. Doctors will often refer patients to mental health professionals who can use specific questions to determine what type of disorder someone might have.
They will ask you about the nature of your symptoms, how long you have been experiencing them, how long an anxiety episode may take, the severity of your symptoms, and more. You will also need to detail exactly how your anxiety symptoms interfere with your ability to function in your daily life.
Treatments for an Anxiety Disorder
Once you get diagnosed with an anxiety disorder, there are a variety of treatment options available. Your doctor or mental health professional can help you determine what is best to help treat your anxiety disorder.
Keep in mind that having an anxiety disorder does not mean you have a weak character; it is not your fault, and it is not something that you can just “get over.” It is a genuine mental health disorder that requires treatment to manage it properly, but with the right treatment, you can manage it and work on preventing it from interfering with your life too much.
-
Medication
There are many different types of medications available that are prescribed to help someone relieve their anxiety symptoms. It is important to keep in mind that not all medications will work for the same people, so it might take a few tries before your doctor or mental health professional helps you find the right prescription for your anxiety disorder. Some of the medications that are most commonly used for an anxiety disorder include:
- Antidepressants. These can help alter the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain, which helps relieve anxiety symptoms.
- Beta-blockers. These are usually used to treat high blood pressure, but they can also help manage the physical symptoms of anxiety.
- Benzodiazepines. These are fast-acting and are usually used as a short-term treatment.
-
Therapy
Therapy can help someone learn ways to manage the behavioral, emotional, and cognitive aspects of their anxiety symptoms. They may be able to help you identify the negative thoughts that can contribute to your anxiety.
A therapist might also try exposure therapy, where they gradually expose you to the things you fear while utilizing relaxation techniques to help soothe the stress in your body. This may be especially helpful for someone with a phobia anxiety.
-
Coping Strategies
There are many different coping strategies that someone with an anxiety disorder can use to help them manage their anxiety. They can try things like getting more sleep, eating healthier, limiting their caffeine intake, and exercising regularly.
Stress management techniques can also help someone manage their anxiety. These include trying yoga, muscle relaxation, or deep breathing to help center themself when they are facing anxiety. There are also plenty of apps for anxiety and panic attack relief that may help someone with these relaxation techniques.
Taking time for yourself and doing something you enjoy can also help with anxiety. You can also try distraction techniques like counting backward from ten. If a project is feeling too big and triggering your anxiety, try breaking it into smaller tasks; you will feel like you accomplished more, and it will not seem too large or overwhelming.
Final Thoughts
If you or someone you know has an anxiety disorder, there are many treatment options available to help manage your symptoms. Treatments can take time to begin working; nothing is going to magically alleviate your anxiety overnight. Be patient and maintain open communication with your doctor or mental health professional to ensure that what you are doing is working.
Geralyn Ritter is an accomplished corporate senior executive, miracle survivor of the 2015 Amtrak train derailment, and author of Bone by Bone: A Memoir of Trauma and Healing. Geralyn is the executive vice president at Organon & Co., a new Fortune 500 healthcare company dedicated to the health of women.